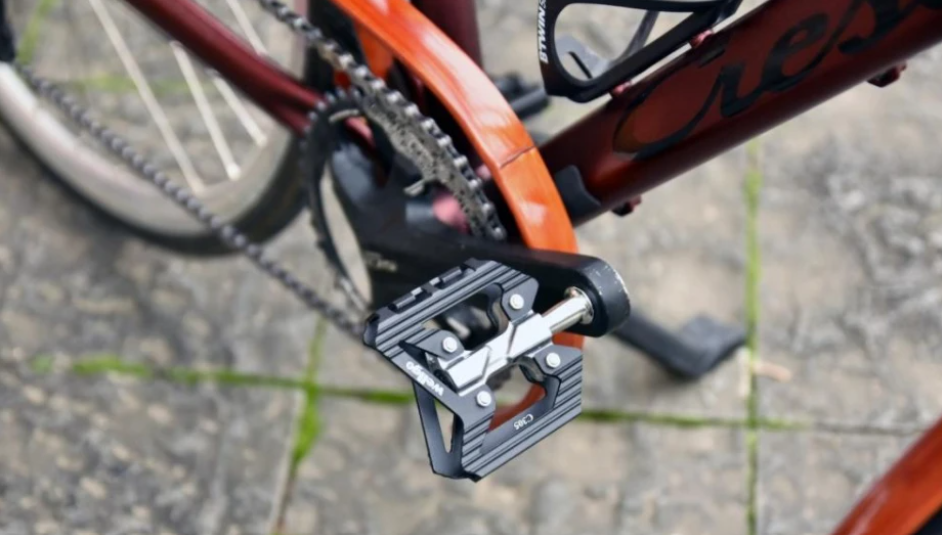
Beginners tend to pay too much attention to the speed when cycling but ignore the most basic cycling skills, such as how to use derailleur correctly, improve your cycling cadence to a certain level, cornering skills, and so on. In this article, let’s talk about the cycling cadence. Many cycling enthusiasts, especially those who have just entered the pit, may not know the concept of cadence. Cadence is a critical parameter in cycling. If you want to be a qualified rider, then you must master your cadence.
What is cycling cadence?
Cadence refers to the number of turns within one minute of the unilateral crank, and the unit of cadence is rpm. It should be noted that cadence refers to the number of turns within one minute of the unilateral curved screen rather than the number of left and right crank turns.
Why should you find a reasonable cycling cadence?
Reasonable cadence can help you save limited energy in your muscles, can also help you reduce the lactic acid accumulation of the leg muscles, let you ride faster and farther with the same energy, but also help you increase the stability of your knee joint, thus reducing unnecessary sports injuries.
The cadence is proportional to the speed of the bicycle; the same speed and tooth ratio under the lower the cadence, the greater the strength required for each step. On the contrary, the higher the cadence, the less power is required for each stampede.

High or low cycling cadence?
In cycling exercise, whether with high or low cadence, two kinds of muscle fibers are fast and slow. Tand they also correspond to different aspects of cycling. Fast muscle fibers correspond to muscle strength in the leg, and slow muscle fibers correspond to our heart and lung function.
Fast muscle fibres use glycogen as fuel to power the body, so they have an anaerobic metabolism. This glycogen is stored in muscles and is relatively low. A Well-trained and energetic athlete they have about 2,000 calories in their body. When fast muscle fibre functions, because it does not need the participation of oxygen, it is easy to produce a large amount of lactic acid accumulation, and it is easy to make the muscle exercise fatigue. And when your body is consumed, it takes a long time to recover.
Slow muscle fibres function the body by burning fat in the body, so it is associated with aerobic exercise. While fat is a significant part of the human body, even a skinny cyclist has much fat to provide sustained body energy. Use slow muscle fiber function because you need oxygen to participate, and the slow muscle fiber vascular network is richer than fast muscle fiber; the myoglobin and mitochondria are much larger than fast muscle fiber, so slow muscle fiber is not easy to produce fatigue at the same time its recovery speed will be breakneck.
How to increase your cycling cadence?
Cycling is a long-distance exercise, and you can’t rely entirely on the anaerobic exercise that fast muscle fibers participate in to complete a 100-mile race. You have to train and improve your cadence to make high cadence and speed up your bike Dio. Usually, beginners’ cadence is about 60 times per minute, which is the most comfortable for ordinary people without deliberate practice, the stampede, and the most labor-saving cadence. However, the fact is that many people ignore their riding cadence, so their cycling speed will always stop there. If you can’t maintain a high cadence for a long time, you will never have a high endurance speed, and practicing a high cadence is dull and counter human.
The high cadence requires a strong bike Dio aerobic capacity to provide continuous energy to the body. It is pretty standard when you suddenly increase your cadence from 60 times per minute to 110 beats per minute within a few minutes. This is when your heart and lung capabilities are improving and strengthening. The process is not only dull but also very painful. If you don’t have strong determination and courage, I suggest you had better give up. Riding slowly is also an excellent way to ride. If you have the determination and courage to make yourself more substantial, you must strictly follow the next advice.
Avoid the power loss occurring during the trampling process.
The stampede in cycling is the circumference of the feet. In the ideal state, the most efficient step is that the direction of force on the feet is always in the tangent direction of the circumference, but this ideal state is impossible. Therefore, in the actual trampling process, the driver cannot always keep the stepping force direction on the circumferential tangent, and the Angle formed by the force direction and the tangent direction forms an ineffective force, which is called the power loss in our daily life. Cadence is pushing the bike forward with as much power as possible.
How to improve your cycling cadence?
Understanding Cadence Training
Cadence training is a long-term training process that focuses on maintaining the body’s stability under high cadence; when the cadence is too high, the body is left and properly shaking and moving up and down. That keeps the driver’s upper body relatively still between the bike. It’s been not easy.
Cadence Standards of Professional Cyclists
If you look closely, you will see that the cadence of professional cyclists usually stays between 100 and 120 times per minute on the flat road, and the cadence of individual time trials increases to between 120 and 150 times per minute. Even on climbs, they keep travelling 80 to 90 times per minute, which can avoid excessive lactic acid in their legs and cause exercise fatigue. A smooth and high-speed stampede is a sign of an experienced driver. He can sit in the upper seat of the bike, while their legs can run at high speed like a piston like an engine continuously generating power. The high cadence of professional drivers is achieved through long-term training. Use a smaller tooth ratio to keep your heart rate below 80% of your maximum heart rate.
Understanding Cadence Training
Cadence training is a long – term training process that focuses on maintaining the body’s stability under high cadence; when the cadence is too high, the body is left and properly shaking and moving up and down. That keeps the driver’s upper body relatively still between the bike. It’s been not easy.
Cadence Standards of Professional Cyclists
If you look closely, you will see that the cadence of professional cyclists usually stays between 100 and 120 times per minute on the flat road, and the cadence of individual time trials increases to between 120 and 150 times per minute. Even on climbs, they keep travelling 80 to 90 times per minute, which can avoid excessive lactic acid in their legs and cause exercise fatigue. A smooth and high – speed stampede is a sign of an experienced driver. He can sit in the upper seat of the bike, while their legs can run at high speed like a piston like an engine continuously generating power. The high cadence of professional drivers is achieved through long – term training. Use a smaller tooth ratio to keep your heart rate below 80% of your maximum heart rate.
Step – by – Step Cadence Training Guide
Step 1: Adjust Seat Height Initially
At the beginning of high – cadence training, lower the seat height of your bike appropriately. After your body gradually adapts, return the seat to its original, correct height. Many people start practicing by beating up and down like sitting on a spring, which consumes a lot of the stability of the core.
Step 2: Focus on Pedal Movement
Focus on the two fixed points during the stampede, the 6 and 12 o’clock. When the pedal is at the lowest point, you should try to pull the pedal back as if you were trying to wipe out the mud stuck to the sole of your shoe. It would help to push the knee forward when the pedal is at its highest point. At the beginning of high – cadence training, lower the seat height of your bike appropriately. After your body gradually adapts, return the seat to its original, correct height.
Step 3: Utilize Cadence – Recording Tools
Use a code table with the cadence recording function as the most direct feedback so that you can observe the current pedal cadence all the time to improve it step by step.
Step 4: Incorporate High – Cadence Intervals
In each ride, spend a certain time with high tread to trample, such as in the last five minutes of the warm – up phase or cycling at the end of the last five minutes. You can try to use between 120 – and 150 – times cadence to trample for a few minutes. Doing so effectively stimulates bikediopulmonary function and helps prevent lactic acid accumulation.
Step 5: Determine Your Optimal Cadence
Find the optimal cadence for you. As an average cyclist, we don’t need to achieve 120 or even 150 rides per minute like a professional rider. We need to find our optimal cadence, which should be the balance point between your muscular system and bike diopulmonary function. When your stepping cadence increases from low to high, your heart rate will also increase; the faster the stepping cadence, the smaller the pedal, so the burden of the muscular system will decrease, and the burden of heart and lung function will increase, so your breathing will become more complex. When you reduce the tread cadence, your breathing becomes comfortable.
However, your thighs tire easily, leading to significant lactic acid buildup. Thus, you need to experiment multiple times to find the optimal tread cadence. This is especially crucial for girls practicing high – tread – cadence cycling. Many girls worry that cycling will make their legs increasingly thick, but that’s not the case. Since high – cadence cycling uses fat as the primary energy source, cycling will make your legs thinner as long as your cadence is high enough.
Step 6: Maintain Optimal Cadence in Different Terrains
Keep your optimal cadence. Because in our actual cycling, not all cycling routes are flat roads, you need to use the derailleur reasonably to maintain the optimal cadence when you encounter small rolling sections. When you go uphill, you need to lower your gear and sacrifice your speed to reduce the intensity of each step. If you can’t continue trampling, try standing up and using your weight to put more pressure on the pedal. When you go downhill, you need to raise your gear to maintain a normal stampede force to avoid a loss of balance and a fall.
What else can a reasonable cycling cadence bring to us?
Others often feel sore knees after cycling. Knee soreness here usually refers to meniscus wear. When your ligaments and muscles cannot support your knee, your stampede can easily cause knee meniscus wear. Therefore, through good tread cadence training, you can exercise and strengthen the muscle group around the knee but also can avoid the wear and tear of the meniscus, thus causing sports injuries to yourself.
BTW, choose the right chainring will always help with your cadence training. Sumlon provides you with all kinds of chainrings, pedals and other bicycle parts.